NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
Looking for easy and reliable NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy? Here you will find clear, step-by-step answers that help students understand important concepts quickly. These solutions follow the latest CBSE guidelines and make revision simple. Whether you want to strengthen your basics or score better in exams, these Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy solutions give you everything you need in one place. Use them to study smarter and learn the complete chapter with confidence.
These solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science. Here we have provided the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy.
In Text Questions
NCERT Textbook Solution for Class 9 Science – Page 148
1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force. Let us take it that the force acts on the object through the displacement. What is the work done in this case?
Answer:
Given,
force, F = 7 N;
displacement, S = 8
We know that, Work done = Force × Displacement
W = F × S
So,
W = 7 × 8
W = 56 Nm
W = 56 J
Hence, the work done in this case is 56J.
NCERT Textbook Solution for Class 9 Science – Page 149
1. When do we say that work is done?
Answer
Work is said to be done when a force applied on an object causes displacement in the direction of that force. If the object moves in the same direction as the force, the work done is positive. If it moves in the opposite direction, the work done is negative.
2. Write an expression for the work done when a force is acting on an object in the direction of its displacement.
Answer
When a force F displaces a body through a distance S in the direction of the applied force, then the work done W on the body is given by the expression:
Work done = Force × Displacement
W = F × s
3. Define 1 J of work.
Answer:
1 J of work is done when a force of 1 N moves an object through a distance of 1 m in the direction of the applied force.
4. A pair of bullocks exerts a force of 140 N on a plough. The field being ploughed is 15 m long. How much work is done in ploughing the length of the field?
Answer:
Given,
Applied force, F = 140 N
Displacement, s = 15 m
We know that,
Work done = Force x Displacement
W= F × s
W= 140 × 15 = 2100 J
Therefore, work done in ploughing the length of the field is 2100J.
NCERT Textbook Solution for Class 9 Science – Page 152
1. What is the kinetic energy of an object?
Answer
The energy possessed by an object due to its motion is called kinetic energy. Every moving object possesses kinetic energy. A body uses kinetic energy to do work.
2. Write an expression for the kinetic energy of an object.
Answer:
The kinetic energy of a body is given by : \( KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2\)
Here m is the mass of the body and v is the velocity.
3. The kinetic energy of an object of mass, m moving with a velocity of 5 m s−1 is 25 J. What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is doubled? What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is increased three times?
Answer:
Given:
- Mass, m = m
- Velocity, v = 5 m/s
- Initial kinetic energy = 25 J
Using the formula for the kinetic energy we have :
\( ⇒ KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2\)
\( ⇒ 25 = \frac{1}{2}m\times5^2\)
\( ⇒ m = 2 kg\)
(i) If velocity is double, v = 2 × 5= 10 m/s
\( ⇒ KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2\)
\( ⇒ KE = \frac{1}{2}m\times10^2\)
\( ⇒ KE = 100 J\)
(ii) If velocity is tripled, v = 3 × 5 = 15 m/s
\( ⇒ KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2\)
\( ⇒ KE = \frac{1}{2}m\times15^2\)
\( ⇒ KE = 225 J\)
NCERT Textbook Solution for Class 9 Science – Page 156
1. What is power?
Answer
Power is defined as the rate of doing work. If W is the amount of work done in time t, then power is given by the expression,
\( Power = \frac{Work}{Time }\)
\( P = \frac{W}{T}\)
The SI unit of power is a watt (W).
2. Define 1 watt of power.
Answer:
When a work of 1 joule is done in 1 s, the power is said to be one watt.
\( P = \frac{1J}{1s} = 1 Watt \)
3. A lamp consumes 1000 J of electrical energy in 10 s. What is its power?
Answer:
Given,
W = 1000J,
t = 10s,
P =?
We know,
\( P = \frac{W}{T}\)
\( ⇒ P = \frac{1000}{10 } = 100 W\)
4. Define average power.
Solution:
Average Power is defined as the total work done divided by the total time taken.
Formula:
\[ E_{\text{avg}} = \frac{\text{Total Work}}{\text{Total Time}} \]
NCERT Textbook Solution for Class 9 Science – Page 158
1. Look at the activities listed below. Reason out whether or not work is done in the light of your understanding of the term ‘work’.
(a) Suma is swimming in a pond.
(b) A donkey is carrying a load on its back.
(c) A wind mill is lifting water from a well.
(d) A green plant is carrying out photosynthesis.
(e) An engine is pulling a train.
(f) Food grains are getting dried in the sun.
(g) A sailboat is moving due to wind energy.
Answer:
(i) Work done by Suma is negative as the force and displacement are in the opposite
direction.
(ii) Work done is zero as the gravity on the load is acting vertically downward whereas its displacement is in a horizontal direction. But it does work while walking against friction between its hoofs and the ground.
(iii) Work done is positive as both force and displacement are in an upward direction.
(iv) Work done is zero as there is no displacement involved.
(v) Work done is positive as the force is acting in the direction of the motion.
(vi) Work done is zero as there is no displacement of the grains.
(vii) Work done by wind force is positive as it supports the motion of the boat.
2. An object thrown at a certain angle to the ground moves in a curved path and falls back to the ground. The initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line. What is the work done by the force of gravity on the object?
Answer:
The work done by gravity depends only on the vertical displacement of the object. Since the initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line, its vertical displacement is zero. Thus work done by vertical forces on the stone will be zero.
Work done by gravity is given by the expression, W = m × g × h
Where,
h= Vertical displacement = 0
W = m g × 0 = 0 J
So, the work done by the force of gravity on the object is zero joule.
3. A battery lights a bulb. Describe the energy changes involved in the process.
Answer:
A battery contains stored chemical energy. When it is connected to a bulb, this chemical energy changes into electrical energy and begins to flow through the circuit. As the electric current passes through the thin filament inside the bulb, the filament becomes hot. This heating makes the filament glow. In this process, electrical energy is converted mainly into heat energy, and a part of that heat is further converted into light energy.
So, the overall energy transformation is:
Chemical energy → Electrical energy → Heat energy → Light energy.
4. Certain force acting on a 20 kg mass changes its velocity from 5 m s-1 to 2 m s-1. Calculate the work done by the force.
Solution:
Given,
Initial velocity u = 5 m/s
Mass of the body,m = 20kg
Final velocity v = 2 m/s
The initial kinetic energy
\( ⇒ E_i = \frac{1}{2}mu^2\)
\( ⇒ E_i = \frac{1}{2}20\times(5)^2\)
\( ⇒ E_i = 10\times25 = 250 J\)
Final kinetic energy
\( ⇒ E_f = \frac{1}{2}mv^2\)
\( ⇒ E_f = \frac{1}{2}20\times(2)^2\)
\( ⇒ E_f = 10\times4 = 40J \)
Since Work done by the force is equal to the change in kinetic energy produced in the body.
Therefore, Work done = Change in kinetic energy
Work done \( = E_f-E_i \)
Work done \( = 40 J- 250J \)
Work done \( = -210J \)
The negative sign shows that the force has reduced the object’s speed, meaning it did negative work.
5. A mass of 10 kg is at a point A on a table. It is moved to a point B. If the line joining A and B is horizontal, what is the work done on the object by the gravitational force? Explain your answer.
Answer:
The work done by gravity is zero. Gravity acts vertically downward, but the object moves horizontally from A to B. Since there is no vertical displacement, gravity does not cause any movement in its own direction.
Work done by gravity is calculated as: \( W = mgh \)
Here, the change in height \( h = 0 \)
So, \( W = mg\times0 = 0 \)
Thus, gravity does no work on the object when it moves horizontally.
6. The potential energy of a freely falling object decreases progressively. Does this violate the law of conservation of energy? Why?
Answer
No. The process does not violate the law of conservation of energy. This is because when the body falls from a height, its loss in potential energy is exactly balanced by a gain in kinetic energy. The total mechanical energy (PE + KE) remains the same throughout the fall. Therefore, the law of conservation of energy is not violated.
7. What are the various energy transformations that occur when you are riding a bicycle?
Answer
When a person rides a bicycle, the food eaten by the rider provides chemical energy, which the body converts into muscular energy. On paddling, the muscular energy changes into mechanical (Kinetic) energy. Also, some energy is released as heat due to friction between the bicycle parts, tires, and road surface.
Thus, the overall transformation is:
Chemical Energy → Muscular Energy → Mechanical (Kinetic) Energy + Heat Energy
8. Does the transfer of energy take place when you push a huge rock with all your might and fail to move it? Where is the energy you spend going?
Answer
When a person pushes a huge rock with full effort but the rock does not move, no work is done because there is no displacement in the direction of the applied force. Since work done is zero, there’s no transfer of muscular energy to the stationary rock. Also, there is no loss of energy because muscular energy is transferred into heat energy, making the person feel warm and tired.
9. A certain household has consumed 250 units of energy during a month. How much energy is this in joules?
Answer
Energy consumed in a month
\( = 250 units \)
\( = 250 kWh \) [ Since1 kWh = 3.6 × 106 J ]
\( = 250 \times 3.6 \times 10^6 \,J\)
\( = 9 \times 10^8\,J\)
10. An object of mass 40 kg is raised to a height of 5 m above the ground. What is its potential energy? If the object is allowed to fall, find its kinetic energy when it is half-way down.
Answer
The potential energy of an object raised above the ground is given by: \( PE = mgh \)
Given,
\( m = 40\ \text{kg} \)
\( g = 9.8\ \text{m/s}^2 \)
\( h = 5\ \text{m} \)
\( PE = 40 \times 9.8 \times 5 = 1960\ \text{J} \)
So, the object possesses 1960 joules of potential energy at a height of 5 m.
At, halfway down, the object is at a height of: \( h = 5/2 = 2.5\ \text{m} \)
Its potential energy at this point is:
\( PE_{\text{halfway}} = 40 \times 9.8 \times 2.5 = 980\ \text{J} \)
At this point, the object has an equal amount of potential and kinetic energy. This is due to the law of conservation of energy. Hence, half-way down, the kinetic energy of the object will be 980 J.
11. What is the work done by the force of gravity on a satellite moving round the earth? Justify your answer.
Answer
When a satellite moves round the Earth, then the direction of force of gravity on the satellite is perpendicular to the direction of its displacement. Hence, the work done on the satellite by the force of gravity is zero.
12. Can there be displacement of an object in the absence of any force acting on it? Think. Discuss this question with your friends and teacher.
Answer
Yes, an object can have displacement without any force acting on it. According to Newton’s First Law, an object in motion continues to move in a straight line at constant speed unless an external force acts on it.
Suppose an object is moving in outer space. With no air resistance and no external force, it will keep moving and cover distance. Therefore, displacement without force is possible when the motion is uniform.
NCERT Textbook Solution for Class 9 Science – Page 159
13. A person holds a bundle of hay over his head for 30 minutes and gets tired. Has he done some work or not? Justify your answer.
Answer
No, the person has not done any work on the bundle of hay. When a person holds a bundle of hay over his head, the person applies an upward force, but the bundle does not move at all. Since there is no displacement, the work done on the bundle is zero, even though the person becomes tired due to the internal effort of his muscles.
14. An electric heater is rated 1500 W. How much energy does it use in 10 hours?
Answer
Given,
Power of the heater = 1500 W = 1.5 kW
Time taken = 10 hours
Energy consumed by an electric heater can be obtained with the help of the expression,
Power = Energy consumed (Work) / Time
Hence,
Energy consumed = Power x Time
Energy consumed = 1.5 x 10
Energy consumed = 15 kWh
Therefore, the energy consumed by the heater in 10 hours is 15 kWh.
15. Illustrate the law of conservation of energy by discussing the energy changes which occur when we draw a pendulum bob to one side and allow it to oscillate. Why does the bob eventually come to rest? What happens to its energy eventually? Is it a violation of the law of conservation of energy?
Answer
When a pendulum bob is pulled to one side, it rises to a higher position and stores energy as potential energy. The moment it is released, this potential energy begins to change into kinetic energy as the bob moves downward. At the mean position, the bob has its maximum kinetic energy and almost no potential energy.
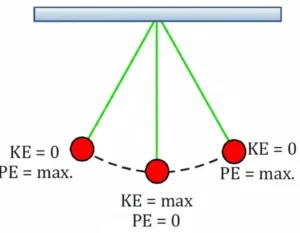
As the bob continues toward the opposite extreme point, the kinetic energy again converts back into potential energy. At that point, the potential energy becomes maximum and the kinetic energy becomes zero. This continuous change between PE and KE shows that the total mechanical energy stays constant, which is the law of conservation of energy.
The bob does not oscillate forever. It comes to rest because air resistance resists its motion.
Thus, the law of conservation of energy is not violated because the energy merely changes its form and is not destroyed.
16. An object of mass, mis moving with a constant velocity, v. How much work should be done on the object in order to bring the object to rest?
Answer
The object is moving with a constant velocity, so it has kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of an object of mass \( m \) and velocity \( v \) is:
\( K.E = \frac{1}{2}mv^{2} \)
To bring the object to rest, all of this kinetic energy must be removed. Therefore, the work that must be done on the object is equal to its kinetic energy but in the opposite direction.
So, the required work is:
\( W = – \frac{1}{2}mv^{2} \)
This is the amount of work needed to stop the object completely.
17. Calculate the work required to be done to stop a car of 1500 kg moving at a velocity of 60 km/h?
Answer
Given,
Mass of car, m = 1500 kg
Velocity of car, v = 60 km/h = 60 × 5/18 ms-1 = 16.67 m/s
We know, Kinetic energy, \( E_k = \frac{1}{2} m(v)^2 \)
\( E_k = \frac{1}{2} \times 1500 \times (16.67)^2 \)
\( E_k = 750 \times 277.8 J \)
\( E_k \approx 208350 \text{ J} \)
\( E_k \approx 2.08 \times 10^{5} \text{ J} \)
To stop the car, an amount of work equal to \( E_k \) is required to be done.
Hence, \( 2.08 \times 10^{5} \text{ J} \) of work is required to stop the car.
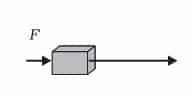
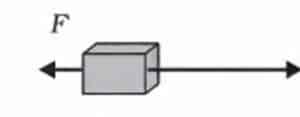
18. In each of the following a force, F is acting on an object of mass, m. The direction of displacement is from west to east shown by the longer arrow. Observe the diagrams carefully and state whether the work done by the force is negative, positive or zero.
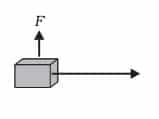

In this case, the direction of force acting on the block is perpendicular to the displacement. So, work done by force on the block will be zero.

In this case, the direction of force acting on the block is in the direction of displacement. So, work done by force on the block will be positive.

In this case, the direction of force acting on the block is opposite to the direction of displacement. So, work done by force on the block will be negative.
19. Soni says that the acceleration in an object could be zero even when several forces are acting on it. Do you agree with her? Why?
Answer
Yes, Soni is correct. An object can have zero acceleration even when many forces are acting on it. This happens when all the forces cancel out each other i.e., the net force acting on the object is zero.
When the net force on an object is zero, the object does not speed up or slow down. It either stays at rest or continues to move with a constant velocity.
20. Find the energy in kW h consumed in 10 hours by four devices of power 500 W each.
Answer
Given,
Power of each device = 500 W = 0.5 kW
Time used = 10 hours
Energy used by one device:
Energy = Power × Time
Energy = 0.5 × 10 = 5 kWh
Since there are four identical devices:
Total energy = 4 × 5 = 20 kWh
Thus, all four devices together consume 20 kWh of energy in 10 hours.
21. A freely falling object eventually stops on reaching the ground. What happens to its kinetic energy?
Answer
When a freely falling object hits the ground, it stops and its kinetic energy becomes zero. However, the kinetic energy is not lost; it is converted into other forms such as heat energy, sound energy, and energy used in deforming the object or the ground.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms And Molecules
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure Of The Atom
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Diversity In Living Organism
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force And Laws Of Motion
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work And Energy
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall ill
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement In Food Resources
