NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1–Matter in Our Surroundings
Are you a Class 9 student looking for Chapter 1 Questions & Answers – Matter in Our Surroundings from Class 9 Science? This article provides complete NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1-Matter in Our Surroundings, explained in simple language. These answers are based on the latest NCERT books and are perfect for your Board exams. After reading the chapter, you may want help with the questions given in it. Here, you can find all the answers in one place. For a better understanding of this chapter, you should also see Class 9 Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings – Summary & Revision Notes. Class 9 Science Chapter 1–Summary & Revision Notes- Matter in Our Surroundings Here we have given Class 9 NCERT Science Textbook Complete Solutions for Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings. For MCQs from this chapter, you should also see. |
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 3
Question 1. Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold-drink, smell of perfume.
Answer: Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
- Chair, air, almonds, and cold-drink are matter because they have mass or occupy space.
- Love, smell, hate, thought, cold, and smell of perfume are not matter because they do not have mass or occupy space
Question 2. Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several meters away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Answer: The smell of hot sizzling food reaches us from several metres away because the particles of matter in hot food have more kinetic energy and diffuse faster in the air. When the food is hot, it gains a lot of energy, and its particles move very fast and spread out quickly into the air around them.
In cold food, the particles move slowly because they have less energy. So, diffusion is slow, and the smell does not travel far. So the smell does not spread far.
Question 3. A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer:
A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. This shows that the particles of water have intermolecular space and has less force of attraction, which allows the diver to move through it easily.
Question 4. What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
Answer. The characteristics of the particles of matter are:
- Particles of matter are very small
Particles of matter have space between them
Particles of matter are continuously moving
Particles of matter attract each other
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 6
Question 1. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density.
(density = mass/volume).
Arrange the following in order of increasing density: air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Answer: The following substances are arranged in increasing density:
Question 2. (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
(b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Answer: (a) Difference in the characteristics of 3 states of matter.
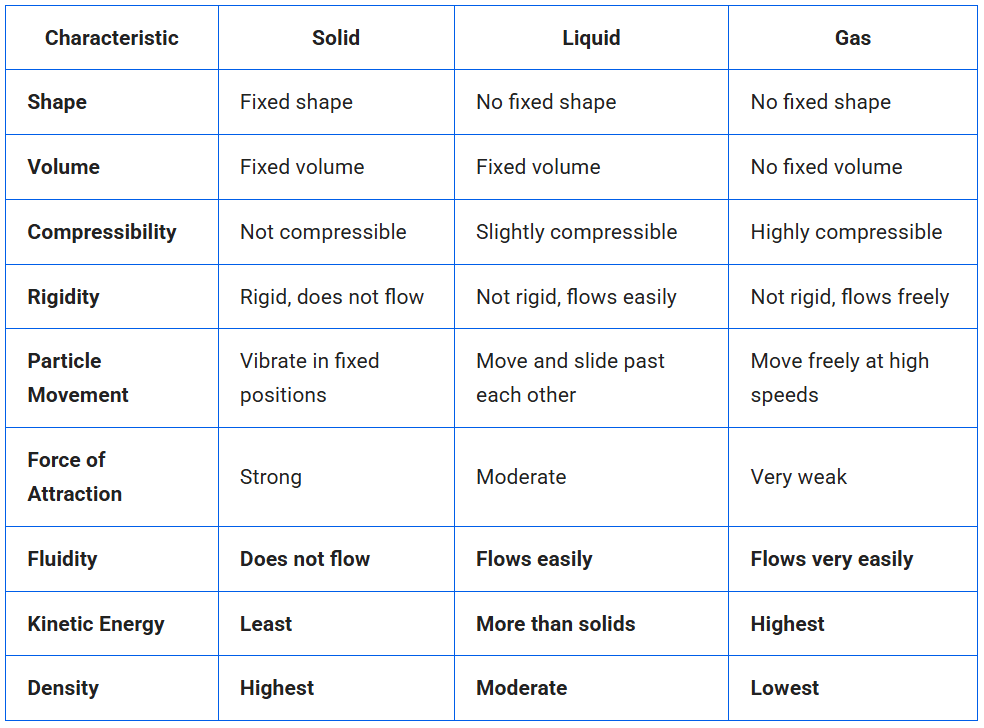
(b) Comment on:
(i) Rigidity: It is the property of matter to maintain its shape even if external forces work. Solids are rigid.
(ii) Compressibility: The property of matter due to which its volume can be decreased by applying pressure. Gases are highly compressible.
(iii) Fluidity: The ability of a substance to flow is called fluidity. Liquids and gases are fluids because they flow easily.
(iv) Filling as a gas container: Gases do not have a fixed shape or volume, so they spread and fill the entire container in which they are kept.
(v) Shape: It is the definite structure of an object. Solids have a fixed shape, while liquids and gases take the shape of the container.
(vi) Kinetic energy: The energy possessed by particles due to their motion is called kinetic energy. The increasing order of kinetic energy possessed by various states of matter are:
Solids < Liquids < Gases
(vii) Density: Mass per unit volume of a substance/matter is known as its density i.e. Density = Mass / Volume.
The decreasing order of density possessed by various states of matter are:
Solids > Liquids > Gases
Question 3. Give reasons
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air but to do the same through a solid block of wood we need a karate expert.
Answer:
(a)A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept because:
The particles of a gas have high kinetic energy and large spaces between them. They have negligible force of attraction. Because of this, gas particles spread out quickly and completely fill the container they are kept in.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container because:
The particles of a gas move randomly at high speed in all directions due to high kinetic energy. While moving, they collide with each other and with the walls of the container. These collisions apply a force on the walls. The continuous hitting of gas particles on the container walls causes pressure on it.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid because:
A wooden table has a definite shape and volume, it does not flow, it is rigid, incompressible
and its particles are tightly packed with very little space between them. The force of attraction between its particles is very strong, all these characteristics are of solid. So wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in the air, but we need a karate expert to move through a solid block of wood because:
In air, the particles are far apart with very weak force of attraction and large spaces between them. So, our hand can move through it easily.
But in a solid block of wood, the particles are very tightly packed with strong force of attraction and very little space between them. That is why it is hard and rigid, and we need a lot of force like a karate expert to break or move through it.
Question 4. Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Answer:
Ice floats on water because ice has a lower density than water. When water freezes into ice, its particles form an open, hexagonal structure with more space between them. This increases the volume and decreases the density of ice. Because ice has lower density, it is lighter than the same volume of water, so it floats on water.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 9
Question 1. Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
(a) 300 K (b) 573 K
Answer.
(a) 300 K
We know, °C=K−273
300 – 273 = 27°C
(b) 573 K
We know, °C=K−273
573 – 273 = 300°C
Question.2. What is the physical state of water at:
(a) 250°C (b) 100°C
Answer:
(a) At 250°C – Water exists in the gaseous state (as steam or water vapour), because this temperature is much above its boiling point (100°C).
(b) At 100°C – Water is in both liquid and gaseous states. At 100°C, water is at its boiling point, so it starts changing from liquid to gas. During this change, both states are present.
Question 3. For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer:
During a change of state (like melting or boiling), the temperature of a substance remains constant because the heat energy supplied is used to break the force of attraction between particles, not to raise the temperature. This hidden heat is called latent heat. Therefore, the temperature stays the same until the entire substance changes its state.
Question 4. Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases?
Answer:
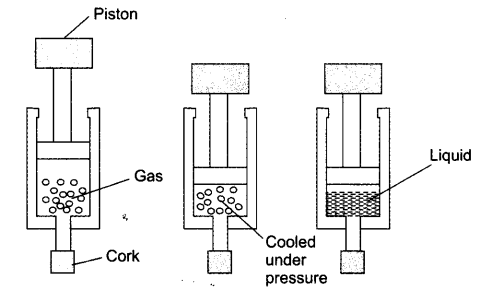
Atmospheric gases can be liquefied by applying high pressure and lowering the temperature. This process brings the gas particles closer, reducing their kinetic energy and converting them into the liquid state. Example: Liquefied Oxygen (LOX) and Liquefied Nitrogen are made using this method.
NCERT Textbook Questions – Page 10
Question 1. Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer:
A desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day because:
- Evaporation depends on humidity. (If there is less water vapor in the air, more evaporation happens). On a hot dry day, the air has low humidity. This allows the water in the desert cooler to evaporate faster and cools the air more.
- The high temperature on a hot day increases the kinetic energy of water particles in the cooler, making them evaporate more quickly and cools the air more.
- Again, during evaporation, water particles absorb heat energy(latent heat) from the surrounding air to change into vapor. This process absorbs more heat from the air, producing a stronger cooling effect.
Question 2. How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
Answer: The water in an earthen pot (matka) becomes cool during summer due to evaporation. The earthen pot has tiny pores in its walls. Water comes out through these pores and evaporates. During evaporation, water takes heat from the remaining water inside the pot, which makes it cool. As a result, the temperature of the water drops, and it becomes cool. This natural cooling method works best in hot and dry weather.
Question 3. Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer:
Our palm feels cold when we put acetone, petrol, or perfume on it because of evaporation.
These liquids evaporate quickly. During evaporation, they take heat from our palm to change into vapour. This loss of heat from the palm causes it to feel cool.
Question 4. Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
Answer:
We can sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer because it has a larger surface area than a cup. As the rate of evaporation is faster with a larger surface area. Tea in a saucer has a larger surface area than in a cup. Therefore, tea cools faster due to faster evaporation. As evaporation increases, more heat is lost, and the tea becomes cool enough to sip quickly.
Question 5. What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
Answer:
In summer, we should wear light-coloured, loose, and cotton clothes. Light colours because it reflect most of the sun’s heat, keeping us cool. Cotton clothes because it has pores in it, which absorb sweat from our body and help it to evaporate quickly. During evaporation, the sweat takes heat from our body and makes us feel cool. Loose clothes because it allow better air circulation, helping in faster evaporation.
Questions From NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science
Question 1. Convert the following temperatures to the Celsius scale.
(a) 293 K (b) 470 K.
Answer:
(a) 293 K into °C
We know, °C=K−273
293 – 273 = 20°C
(b) 470 K into °C
We know, °C=K−273
470 – 273 = 197°C
Question 2. Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale.
(a) 25°C (b) 373°C.
Answer:
(a) 25°C into K
We know, °C=K−273
∴ °C + 273 = K
25 + 273 = 298 K
(b) 373°C into K
We know, °C=K−273
∴ °C + 273 = K
373 + 273 = 646 K
Question 3. Give reason for the following observations.
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Answer:
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time because they change directly from solid to gas without becoming liquid. This process is called sublimation. So, they slowly sublime into the air and leave no solid behind.
(b) The perfume contains volatile particles that evaporate quickly into the air. These particles mix with air molecules and spread out due to diffusion. As a result, the smell reaches our nose even when we are sitting several metres away.
Question 4. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles—water, sugar, oxygen.
Answer:
Oxygen (gas) < water (liquid) < sugar (solid)
Question 5. What is the physical state of water at—
(a) 25°C (b) 0°C (c) 100°C
Answer:
(a) 25°C – Liquid
At 25°C, water is in the liquid state, as it is above the melting point (0°C) and below the boiling point (100°C).
(b) 0°C – Solid and Liquid (both)
At 0°C, water can be in both solid and liquid states, as this is its melting point, where it changes from solid to liquid or vice versa.
(c) 100°C – Liquid and Gas (both)
At 100°C, water can be in both liquid and gaseous states, as this is its boiling point where it changes from liquid to gas.
Question 6. Give two reasons to justify
(a) water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer:
(a)
- Water persists as a liquid at room temperature (say 25°C) since its melting point (0°C) is lower than room temperature and its boiling point (100 °c) is higher than room temperature.
- Water has no fixed shape but a fixed volume, and it flows easily, which is a property of liquids. So, at room temperature water shows the characteristics of a liquid.
(b)
- The melting point and boiling point of iron are above room temperature. Therefore, an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
- An iron almirah has a fixed shape and volume, and it is rigid and cannot be compressed, which are key characteristics of solids, so we can say that an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Question 7. Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer:
When ice is at 273 K, it is at its melting point. Ice needs to absorb a large amount of heat, called the latent heat of fusion, to change into liquid water. This heat comes from the surroundings, making the surroundings colder. Water at 273 K doesn’t need this extra heat, so it absorbs less heat and cools less effectively.
Question 8. What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer:
Steam contains extra energy in the form of latent heat of vaporisation. When steam condenses on the skin, it releases this latent heat along with its own heat (at 100°C). Boiling water is also at 100°C, but does not have this extra latent heat. Therefore, steam transfers more heat to the skin and causes more severe burns.
Question 9. Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state
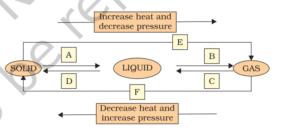
Answer:
(A) Solid to Liquid → Melting (or) fusion (or) liquefaction
(B) Liquid to Gas → Evaporation (or) Vapourisation
(C) Gas to liquid → Condensation
(D) Liquid to Solid → Solidification
(E) Solid to Gas → Sublimation
(F) Gas to Solid → solidification
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms And Molecules
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure Of The Atom
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Diversity In Living Organism
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force And Laws Of Motion
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work And Energy
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall ill
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement In Food Resources
